Google Search Console: The Ultimate Guide for 2025
Explore 'Google Search Console: The Ultimate Guide' to master the essentials of optimizing your website's performance. Learn how to leverage powerful tools and features to monitor site traffic, fix issues, improve SEO, and drive bulk traffic. Enhance your site's visibility on Google with expert insights and actionable tips.

-
What Is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool that helps you track and enhance your website's search performance and technical SEO.
With GSC, you can monitor various metrics like search appearance and user experience, which can help you boost your site's traffic from Google.
Here's what you can do with GSC:
- Check your site's performance on Google
- See which pages are indexed by Google
- Submit sitemaps and URLs for crawling
- Identify and fix technical SEO issues
- And much more!
In this guide, we’ll show you how to use Google Search Console to improve your SEO.
Let’s dive in!
-
How to Set Up Google Search Console
First, sign in to Google Search Console with your Google account.
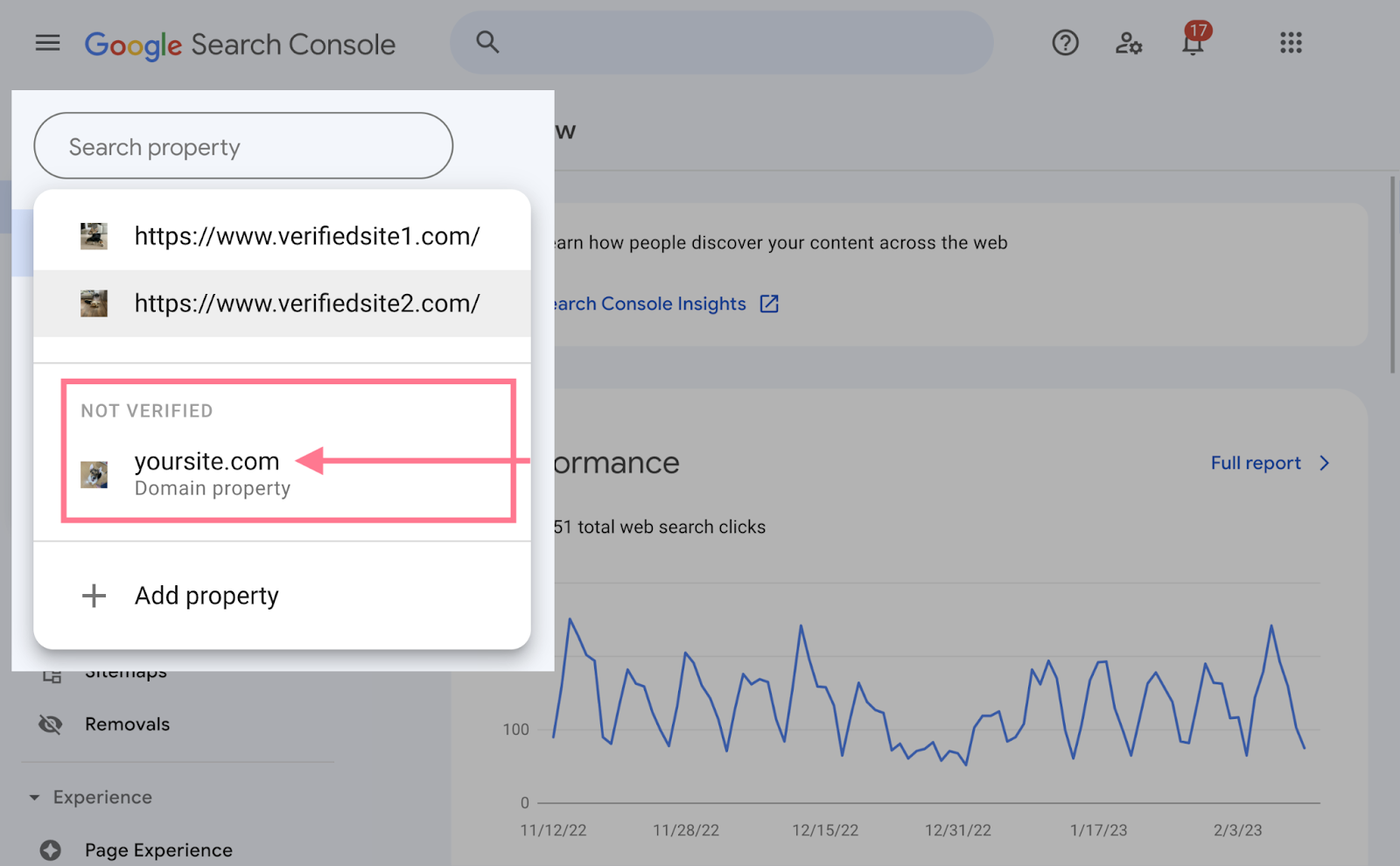
When you log in for the first time, you'll see a pop-up asking you to add a property (your website).

You have two options here: add a domain or a URL prefix.
Add a Domain Property
Adding a domain property will give you the most comprehensive view of your website’s information.
You'll receive data from all URLs under the domain name, including all protocols, subdomains, and paths.
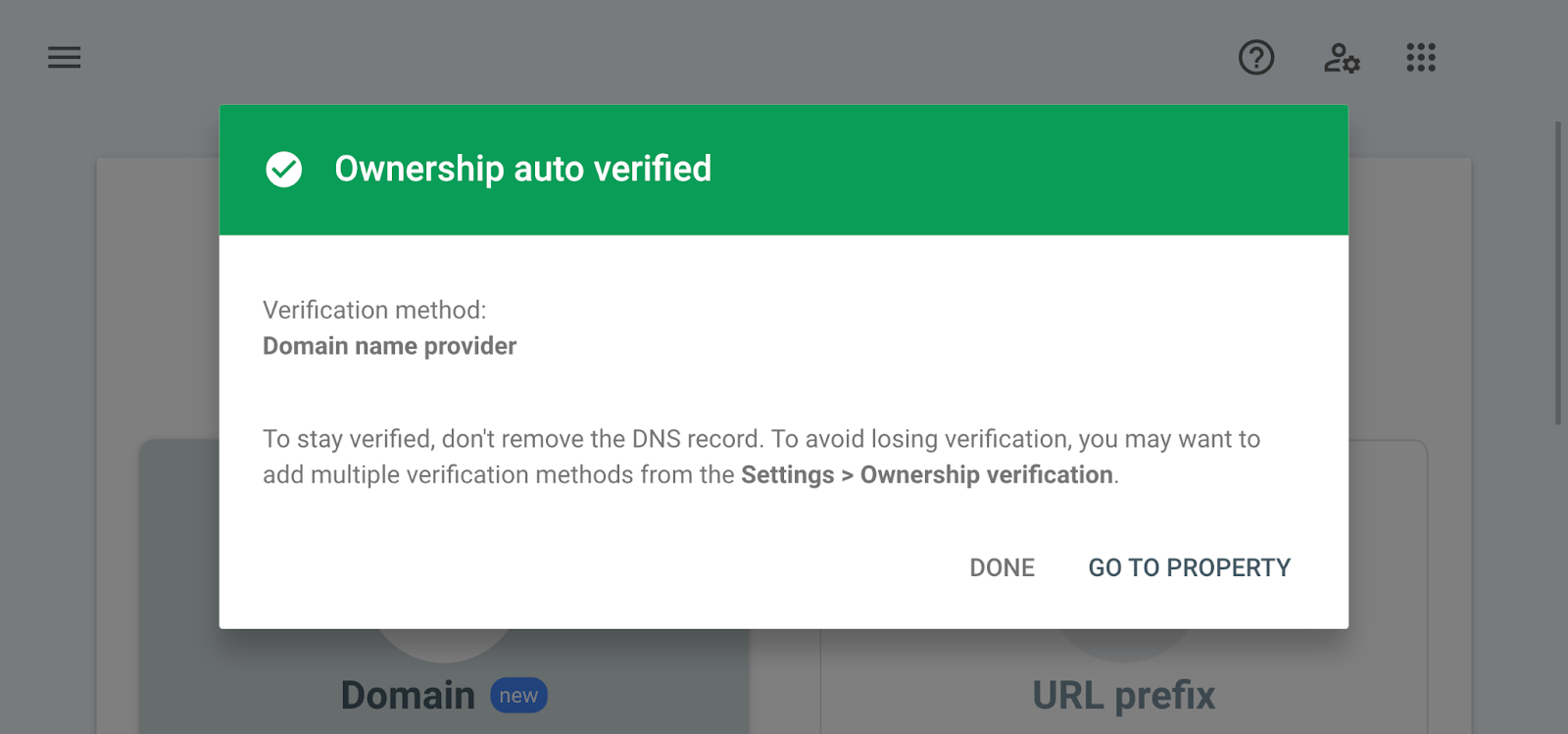
To add a property this way, you'll need to verify it through your DNS (domain name system) provider.
Here’s how to do it:
- Add your domain in the “Domain” option (without HTTP/HTTPS and www).
- For example, if your domain URL is “https://www.yoursite.com,” enter “yoursite.com” in the blank space provided.
- Click “CONTINUE.”
This setup ensures you get a complete overview of your site's performance.

Then, copy the TXT record from the instructions dialog box.

In a new tab, sign in to your account with your domain registrar. For this example, we'll use GoDaddy.
Once you log in, access your DNS settings by clicking on the nine dots in the navigation bar next to your business name and selecting “Domains.”

In your Domain Portfolio dashboard, select the three dots beside your domain name and click on “Edit DNS.”

You should now be in the DNS Management window. Add a new TXT record by clicking “Add” in the DNS Records section.

A form will pop up. Fill it out as follows:
- Type: TXT
- Name: @
- Value: [Paste the TXT record from Google Search Console]
- TTL: 1 hour

When you’re done, click “Add record.”

Now go back to Search Console and click “Verify.”

-
Owners, Users, and Permissions
You can have one of two roles in a Search Console account: owner or user.
Your permissions depend on your role.
Owners: Owners have full control over the property in Search Console. They can add or remove users, view all data, configure settings, and use all tools within Search Console. There are two types of owners:
- Verified Owner: Verified owners have proven ownership of the property using a verification token (like an HTML file or tag).
- Delegated Owner: Delegated owners are granted access by verified owners.
Users: Users have more limited permissions compared to owners.
- Full User: Full users can view all data for a property and take certain actions.
- Restricted User: Restricted users have partial access and may not be able to view all available data.
- Associates: Associates cannot directly access or view your Search Console account or data but can perform other tasks depending on the type of association.
If you’re the property owner, you can add new users and grant permissions. To add a new user, navigate to “Settings” > “Users and permissions.”

Click “ADD USER.”

Enter the new user’s email address and select the access type. Then, click “ADD.”

The newly added user can now access your property in the Search Console.
-
How to Add a Sitemap to Google Search Console
A sitemap file includes all the website URLs you want Google to crawl and index. This is important for Google to rank your pages. While Google will eventually crawl and index your site, submitting an XML sitemap directly via Google Search Console (GSC) can speed up the process.
To submit your sitemap:
- Click “Sitemaps” on the navigation sidebar.
- Enter the sitemap URL in the provided field.
- Click “Submit.”

Once Google is done processing your sitemap, you’ll see a message like this:

-
Google Search Console Reports and Features
Now that you’ve activated Search Console for your website, added users, and submitted a sitemap to Google, it’s time to explore the different reports and features available.
Performance Report
The “Performance” report provides data on how your website is performing on Google. It shows four key metrics:
- Total clicks: The number of times people clicked on your site from the search results.
- Total impressions: The number of times your site appeared in search results.
- Average CTR (click-through rate): The percentage of impressions that resulted in a click.
- Average position: The average position of your site in search results.
To review these metrics for your site, click “Search results” from the sidebar navigation.

Below the chart, you’ll see a table displaying the queries, pages, countries, and devices driving traffic to your site. It also provides information on page experience and the number of clicks you received by date.

Here are two ideas to consider when analyzing your Google performance data:
Low CTR: If your pages rank well but don’t get many clicks, try writing better title tags and meta descriptions. This will make your pages more appealing to users.
Missing Keywords: If you don’t rank for important keywords, your site might not have enough useful content addressing them. Improve your content strategy and produce quality content targeting the terms you want to rank for.
If your website receives traffic from Discover and Google News, you’ll also see specific reports for these segments.
The reports will look similar to the main performance report, showing metrics like clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position.

URL Inspection Tool
The “URL inspection” tool helps you check the index status of individual pages on your website and troubleshoot issues that may be preventing your page from appearing in Google’s search results.
Access the tool from the top bar or by clicking “URL inspection” from the navigation bar.