Understanding Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs)
Understand the intricacies of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) with our detailed guide. Learn how to optimize your content for better rankings, drive bulk traffic, and increase visibility. Discover tips and strategies to make the most out of SERPs for your SEO efforts

-
What Is SERP?
-
What’s on a Google SERP? And How Do SERP Rankings Work?
Search engine results pages can include three types of listings:
Organic search results, which look like this,
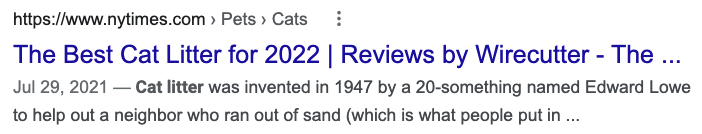
Paid search results, which are identified with the word “Ad:”,

And SERP features can show up in many different ways. One common SERP feature is the “People Also Ask” box, which looks like this:

Let’s take a closer look at all three types of search results.
We’ll discuss where they come from and how they affect SEO.
Organic Search Results
Google handles trillions of searches per year.
Remarkably, 95% of the clicks from those searches go to the organic (unpaid) search results.
This is why interest in SEO has been growing continuously.

Most of SEO boils down to one concept:
The higher a search result is shown on the SERP, the more people tend to click on it.
The #1 ranking result is shown at the top of the SERP, so it usually gets the most clicks. This is followed by #2, and so on:

How much do rankings matter, exactly?
A lot.
Here are the average click-through rates on Google by ranking position, according to a study by Backlinko:
- 31.73%
- 24.71%
- 18.66%
- 13.60%
- 9.51%
And the drop-off continues from there. The #1 ranking usually gets 10x more clicks than the #10 ranking.
So how does a page get ranked #1?
Google relies on hundreds of different ranking factors to decide, but you can divide them into two major categories:
- Off-page SEO factors: Like backlinks to the page.
- On-page SEO factors: Like the page’s content and meta tags.
On-page factors also affect something else: the appearance of the search results. Specifically, they control the search result “snippet” that’s shown on the SERP.
A basic search snippet consists of three things:
- The URL or breadcrumbs, are based on the page’s URL and navigational links.

- The title link is usually based on the page’s meta title tag.

- And the description, which is usually based on the page’s meta description.

That’s the basic structure.
But some search snippets are more complex than that.
For example, here is the top result for the search query “best camping stove.”
You can see it has a few additional parts:
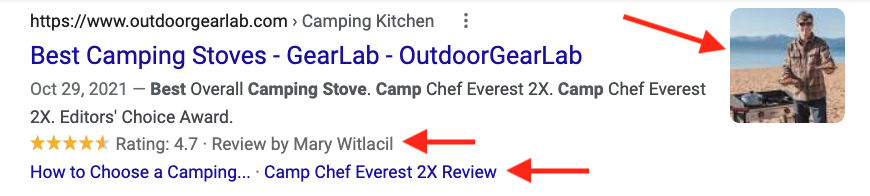
Unlike our basic search snippet, this one has:
- An image on the side
- A star rating in the middle
- Additional links (called “site links”) at the bottom
Extra pieces of information like those are called “rich snippets.” They make the search result stand out, which can increase its CTR and traffic.
In other words, rich snippets are one of the ways you can get more visits from a SERP—even without improving your rankings.
(SERP features are another way. But we’ll come back to those in a minute.)
Paid Search Results
Paid search results are the second type of listing that can appear on a SERP. On Google, paid search results are managed via Google Ads and are paid for on a cost-per-click basis.
Google Search Ads are often shown at the top of the SERP above all the organic results, like this:

Search ads can also be displayed at the bottom of the SERP, after the organic results:
Some SERPs display Google Shopping Ads, which e-commerce stores use to advertise their products. These ads usually show up when you search for a physical product.
Google Shopping Ads look quite different from regular search ads. They contain less text and include images, providing a more visual experience for users.
Google Shopping Ads can appear at the top, bottom, or in the middle of the SERP, or off to the side, like this:

SERP Features
SERP features are the third type of result you’ll see in the SERPs. A SERP feature is anything that isn’t a regular organic or paid search result.
For example, here’s a “Featured Snippet” about the largest star in the universe:

Like regular organic search results, SERP features are unpaid. Google refers to SERP features as "search features." According to Google, their purpose is to provide people with "the right information at the right time in the format that’s most useful."
However, many marketers view SERP features as competition because they draw attention and clicks away from regular organic search results. Only about one-third of all Google searches now result in a click on an organic result, with SERP features being a major reason why.
SERP features can even create a significant difference in search traffic between two very similar keywords, sometimes a very big difference, even when the keywords have the same search volume.
For example, let’s compare the keywords “mortgage comparison” and “affordable mortgages."
Consider both keywords get 1,600 searches per month. And both keywords have to do with mortgages.
However, their SERPs are completely different. The SERP for “mortgage comparison” is pretty traditional. It shows four search ads at the top and then goes straight into the regular organic results.

The SERP for “affordable mortgages” is a different story. It starts with ads at the top, like the other SERP, but then it shows two separate SERP features:
- A “Local Pack” of Google Maps results
- A “People Also Ask” box of questions
All this appears before the regular organic results. Look how far you have to scroll before you can see the first organic result on this SERP:

As mentioned, both of those keywords get 1,600 searches per month.
However, the differences in their SERPs change their “Click Potential” significantly.
Click Potential is the predicted chance of getting a click-through to the regular organic results.
So it’s a good idea to look at the Click Potential for any keyword before deciding whether to target it. Additionally, examine the SERP itself to understand which SERP features you'll be up against. This will help you make informed decisions about your SEO strategy and maximize your chances of getting clicks.
Now you’ve seen the negative impacts that SERP features can have. Here’s the thing:
You can also use SERP features to your advantage. It’s often easier to win a SERP feature than it is to climb the standard organic rankings. So you can use SERP features to leapfrog high-authority competitors.
Let’s look at a quick example:
The SERP for the keyword “email service provider.” The regular organic rankings for this keyword include huge sites like Active Campaign and TechRadar.

Active Campaign has around 72 Authority Scores and TechRadar has 80 Authority Scores. These sites have high Authority Scores, making them hard to beat in the regular rankings
But above those big competitors, Google is displaying a Featured Snippet. And that Featured Snippet belongs to a much smaller website called Clean Email.

Thanks to that Featured Snippet, Clean Email is getting a large share of traffic from this keyword, despite having a much lower Authority Score than its larger competitors.
That’s a positive example of the power of SERP features.
And we’re still only scratching the surface—there are over 20 different types of SERP features.
Let’s cover some of the most common and important ones so you can avoid competing against them and use them to your advantage instead.
-
Top SERP Features: Essential Elements You Need to Know
Featured Snippet
A Featured Snippet is a prominent highlight that Google takes from a single webpage to summarize the most important information. You’ll often see Featured Snippets at the very top of the organic SERP, in “position #0,” making them one of the most powerful SERP features.
They can also appear when you expand a “People Also Ask” box.
There are several types of Featured Snippets. Many are text-heavy, like this list-based Featured Snippet for “best premium SEO software:”

Other Featured Snippets include images.
Here’s the one for the search query “impressionism:"

And some Featured Snippets suggest a clip from an embedded video.
Like this one for the keyword “how to sprint:"

People Also Ask
People Also Ask boxes list several questions related to the original search query. They are usually shown for keywords with commercial or informational search intent.
Here’s the People Also Ask box that gets displayed when you search for “scheduling software:”

When you click on a question in a People Also Ask box, it expands to reveal a Featured Snippet inside, along with a link to launch a new Google search using that question.
Like this:

Related Searches
Related Searches are keywords connected to your original search query. When you click on one, Google opens a new SERP using that keyword.
Related Searches are displayed at the bottom of the SERP and are extremely common. Most people don’t even think of them as a SERP feature.
The most basic version of the Related Searches feature is simply a list of keywords. However, some Related Searches also include images above the keywords. As you can see in this example from the keyword “best premium SEO tool:”

Knowledge Panel
According to Google, Knowledge Panels appear when you search for entities that are in Google’s Knowledge Graph. A single Knowledge Panel includes information from multiple different sources.
Knowledge Panels are displayed on the right-hand side of the search results. They often display:
- Associated images
- A text description
- A list of facts
- Links to additional information
Here’s the Knowledge Panel for the search query “Android:”

Local Pack
Local Packs display information about nearby businesses and organizations next to an embedded map from Google Maps.
Local Packs are displayed for search queries that might relate to a local need, showing different results depending on the searcher's location.
This Local Pack is shown at the top of the SERP when someone in New York City searches for “bowling alley:”

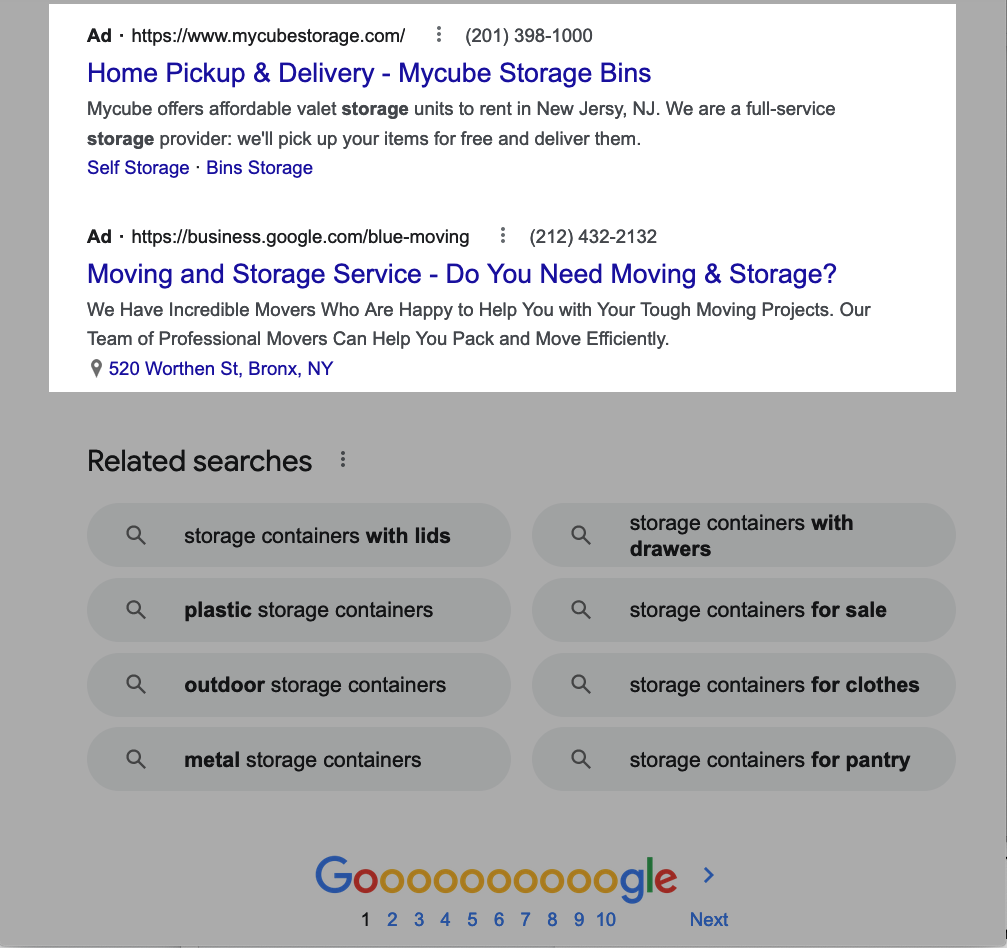
Local Packs can also appear for search queries that don’t have such obvious local search intent, but they’ll usually be farther down on the SERP in that case.
For example, the bottom of the SERP for “glass storage containers” displays the following Local Pack:

Google Flights
For search queries about flights, Google often displays a Google Flights SERP feature.
The Google Flights SERP feature can be interactive, like this one for the keyword “NYC to PDX:”

Or it can be more basic, like this one for the keyword “flights to Oregon:"

Organic Google Shopping Results
Organic Google Shopping results look a lot like Google Shopping Ads, which we already saw in the “Paid Search Results” section above. However, organic Google Shopping results are unpaid and don’t have the “Ad” disclaimer.
Organic Google Shopping results are usually displayed as a carousel of products you can scroll through. They can appear anywhere in the main SERP.
Each organic Google Shopping result can contain:
- An image of the product
- The product name and brand
- The retailer
- The price
- The average star rating
- A fact or two about the product
Here’s the organic Google Shopping results carousel for the keyword “home printers:”

Image Pack
Image Packs are a way for Google to display images on the SERP. Clicking on one will take you to a Google Images search results page.
Image Packs can be shown anywhere in the regular search results and sometimes are displayed as scrollable carousels. They can appear as a single row or in a larger pack.
Here’s the Image Pack for the keyword “Iceland:”

And below is a larger Image Pack that displays for the keyword “Nike shoes." In this case, some of the images have a shopping tag icon, indicating that the image was taken from a retailer’s product page.

Video Results
Video Results are exactly what they sound like a pack of videos on the SERP. The videos usually come from YouTube.
Each video listing can be paired with links to specific timestamps within it, as you can see in this example:

Recipes
The “Recipes” SERP feature can be displayed when you search for recipes. It displays a pack of three recipe options, along with a button to show more.
Here’s the one for “fried rice recipe:”

Direct Answers
Direct Answers present a short piece of information at the top of the SERP. They can be displayed when Google believes the query is a simple question.
For example, “when is Mother’s Day:”

Top Stories
Top Stories displays relevant articles from Google News. For queries that are clearly about the news, the Top Stories feature is usually shown at the top of the SERP. For other queries, it may be shown lower down.
Here’s today’s Top Stories pack for the query “financial news:”

-
Concluding
As you can see, there’s no such thing as a standard SERP. Search engine results pages can change drastically from keyword to keyword and from location to location. They can also be personalized based on user behavior.
But now that you understand how they work, you can take the next step in your SEO journey.
If you’re a beginner, get started with our introduction to learning SEO.
Or jump into the deep end with our detailed guides to on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.









